The steps below show how to use the DISKPART command line tool to reformat the USB drive. You will need local administrator access on the computer to follow these steps. The process will involve wiping the USB drive – back up before progressing.
- On your keyboard, press the Windows button + R
- type DISKPART and click ‘OK’
- Click ‘Yes’ if prompted by the User Access Control
- DISKPART will open in a command prompt window
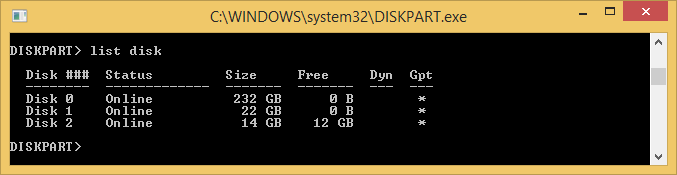
- Type list disk and hit enter
- You will need to identify your drive by size, in this case I can see it is disk 2
- Type select disk 2 (where 2 is the number from the previous step)
- The command prompt will respond by saying “Disk 2 is now the selected disk”
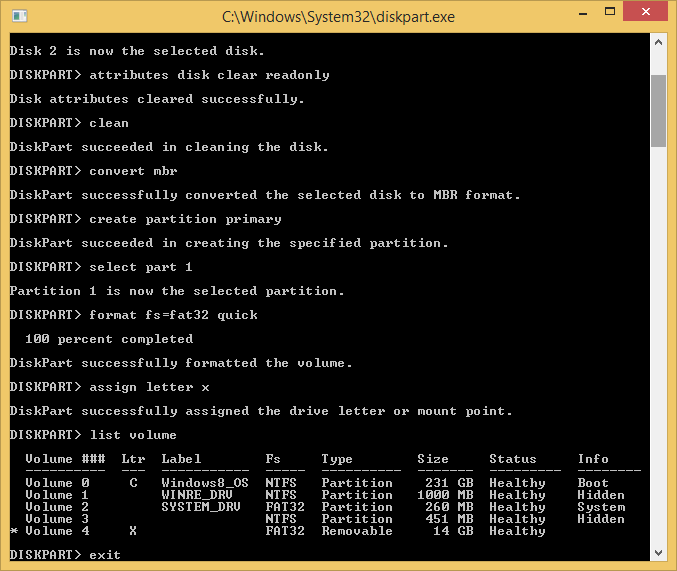
- Now enter the following commands (if your disk is a USB drive, I recommend sticking with fat32 for the best compatibility across different operating systems. If your disk is a system drive use NTFS instead, e.g. format fs=ntfs quick)
-
attributes disk clear readonly clean convert mbr create partition primary select part 1 format fs=fat32 quick assign letter x list volume
- Type exit and hit enter to close the window.
- You drive will now be reformatting using the full capacity as FAT32
Help – it didn’t work !
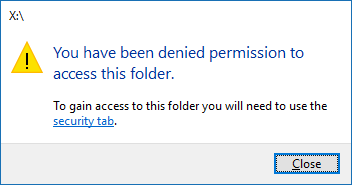
Denied permission
After completing these steps, if you get an access denied message when opening the drive – try removing and re-inserting the drive.
I still can’t access the drive!
For some reason this doesn’t work first time.
If you still can’t access to drive:
- Unplug and plugin the USB drive again
- Repeat the instructions above